







|
|
|
 |
cDNA Microarray Imaging
Registering the scanned monochrome images corresponding to the
experimental and control channels produces a two channel Red-Green (RG)
image. Such a cDNA microarray is a vector (multichannel) signal which
can be represented, for storing or visualization purposes, as RGB
color image with a zero blue component. |
 |
|
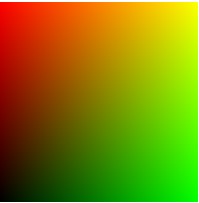
Each sample of the cDNA microarray image
can be considered as point, defined by its intensity values in the red and
green channel, in a two-dimensional, RG vector space. Thus, each cDNA sample
represents a two-dimensional vector which is uniquely determined by its
magnitude and direction in the RG vector space. This suggests that cDNA
microarray images can be processed according to their magnitude and
directional characteristics. However, due to the numerous noise sources
affecting the cDNA microarray image formation, any processing task on such
vectorial data is rather
difficult and challenging. |
|
References: |
|
 | R. Lukac and K.N. Plataniotis, "cDNA Microarray
Image Segmentation Using Root Signals," International
Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, vol. 16, no. 2,
pp. 51-64, April 2006. |
 | R. Lukac, K.N. Plataniotis, B. Smolka, and A.N.
Venetsanopoulos, "A Multichannel Order-Statistic Technique for
cDNA Microarray Image Processing," IEEE Transactions on NanoBioscience,
vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 272-285, December 2004. |
|
|
|
